High-carbon steel strip: Bainitic hardened
| Classification of symbols | Numerical classification | European Standard (EN) | Chemical Composition | |||||||
| C | Si | Mn | Max. P | Max. S | Cr | V | Ni | |||
| C60S | 1.1211 | EN 10132-4 | 0.57 - 0.65 | 0.15 - 0.35 | 0.60 - 0.90 | 0.025 | 0.025 | max. 0.40 | - | max. 0.40 |
| C67S | 1.1231 | EN 10132-4 | 0.65 - 0.73 | 0.15 - 0.35 | 0.60 - 0.90 | 0.025 | 0.025 | max. 0.40 | - | max. 0.40 |
| C75S | 1.1248 | EN 10132-4 | 0.70 - 0.80 | 0.15 - 0.35 | 0.60 - 0.90 | 0.025 | 0.025 | max. 0.40 | - | max. 0.40 |
BAINITIC HARDENED STRIP: HIGH STRENGTH AND DUCTILITY
CHEMICAL COMPOSITIONS AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Bainitic hardened steel strip is obtained by means of a heat treatment that consists of rapid cooling of the steel piece from a high temperature. To achieve this result, the strip is kept at an intermediate temperature for a certain time, forming a bainitic structure. The main characteristic of bainitic hardened strip is its ductility, so that the material can be deformed without breaking. In addition, this type of strip has high hardness and mechanical strength.
Among the options available at VINCO for bainitic hardened steel strips are the following chemical compositions: C60S with 0.57-0.65% quenched carbon and good mechanical strength; C67S containing 0.65-073% quenched carbon with high strength and hardness; C75S composed of 0.70-0.80% carbon and quenched steel. The latter is characterized by a good combination of strength and flexibility.
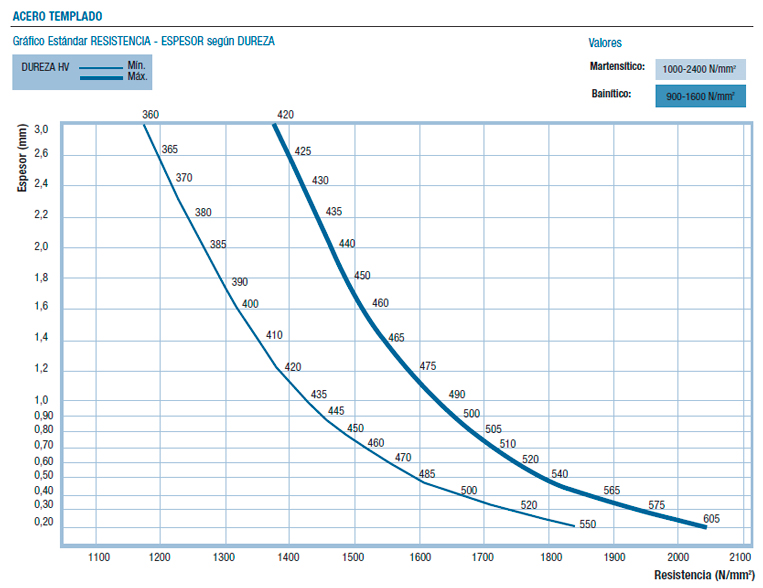
In the "Mechanical properties" section of the product sheet you can check the difference between bainitic hardening and martensitic hardening according to the thickness and strength of the material. The mechanical properties of this type of strip are agreed at the time of order. Please contact our team of experts so that they can advise you according to your needs on the contact telephone number (+34) 94 412 33 99 or send us an email to info@vinco.es.

FINISHES AND TOLERANCES FOR BAINITIC HARDENED STRIP
High carbon steel strips such as banitic hardening have finishes subject to the EN 10132-4:2000 standard that applies to cold-rolled strips for heat treatment. The surface finish or roughness of the strip is determined at the time of the order according to your needs.
The tolerances for this type of strapping are detailed in the product sheet and are divided into: thickness tolerances, width tolerances, length tolerances and arrow tolerances, which refer to the arching of the strapping strips. In addition, the flatness tolerance for strip strips is also detailed.
VINCO is ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 certified for the cutting and marketing of steel strips. This reflects that we work under quality standards throughout the delivery process, always meeting the needs of our customers.
| Classification of symbols | Numerical classification | European Standard (EN) | Approximate international equivalents | |||||
| US (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | China (GB) | ||||||
| C60S | 1.1211 | EN 10132-4 | ||||||
| C67S | 1.1231 | EN 10132-4 | 1065 | A505/506 | SUP 10 | G4802 | 70 | GB/T 1222 |
| C75S | 1.1248 | EN 10132-4 | 1074 | A682/684 | - | - | - | - |
| Classification of symbols | Numerical classification | European Standard (EN) |
| C60S | 1.1211 | EN 10132 |
| C67S | 1.1231 | EN 10132 |
| C75S | 1.1248 | EN 10132 |
- The mechanical properties are not specified in any standard on the date of publication of this information.
- The mechanical properties must be agreed when placing the order.
- The typical values fall within the range of 900-1400N/mm2.
- The hardness/tensile strength specification must fall within a range of 150 N/mm² or 50 HV, unless stated otherwise in the commercial agreement.
For information purposes, the table below shows the difference between austempering and martensitic hardening.
EN 10132-4:2000
- The requirements regarding roughness can be agreed when requesting the quote or placing the order.
THICKNESS TOLERANCES
| Nominal Thickness t | Thickness tolerances according to EN 10140 for nominal widths w of | ||||||
| <125 | ≥ 125 and <600 | ||||||
| > | ≤ | A normal | B fine | C precision | A normal | B fine | C precision |
| - | 0.10 | ± 0.008 | ± 0.006 | ± 0.004 | ± 0.010 | ± 0.008 | ± 0.005 |
| 0.10 | 0.15 | ±0.010 | ± 0.008 | ± 0.005 | ± 0.015 | ± 0.012 | ± 0.010 |
| 0.15 | 0.25 | ±0.015 | ± 0.012 | ± 0.008 | ± 0.020 | ± 0.015 | ± 0.010 |
| 0.25 | 0.40 | ± 0.020 | ± 0.015 | ± 0.010 | ± 0.025 | ± 0.020 | ± 0.012 |
| 0.40 | 0.60 | ± 0.025 | ± 0.020 | ± 0.012 | ± 0.030 | ± 0.025 | ± 0.015 |
| 0.60 | 1.00 | ± 0.030 | ± 0.025 | ± 0.015 | ± 0.035 | ± 0.030 | ± 0.020 |
| 1.00 | 1.50 | ± 0.035 | ± 0.030 | ± 0.020 | ± 0.040 | ± 0.035 | ± 0.025 |
| 1.50 | 2.50 | ± 0.045 | ± 0.035 | ± 0.025 | ± 0.050 | ± 0.040 | ± 0.030 |
| 2.50 | 4.00 | ± 0.050 | ± 0.040 | ± 0.030 | ± 0.060 | ± 0.050 | ± 0.035 |
| 4.00 | 6.00 | ± 0.060 | ± 0.050 | ± 0.035 | ± 0.070 | ± 0.055 | ± 0.040 |
Sizes in mm.
WIDTH TOLERANCES
| Width tolerances for strips with sheared edges | Standard slitting tolerances for VINCO 1) | Width tolerances according to the EN 10140 Standard for nominal widths of: | |||||||||
| Nominal Thickness t | 3-15 | 15-50 | 50-150 | >150 | <125 | ≥ 125 and <250 | ≥250 and <600 | ||||
| >= | < | A | B | A | B | A | B | ||||
| 0.1 | 0.4 | ± 0.075 2) | ± 0.075 2) | ± 0.075 2) | ± 0,10 2) | ± 0.15 | ± 0.10 | ± 0.20 | ± 0.13 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.18 |
| 0.4 | 0.7 | ± 0,085 | ± 0,09 | ± 0,10 | ± 0,12 | ± 0.15 | ± 0.10 | ± 0.20 | ± 0.13 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.18 |
| 0.7 | 1.0 | ± 0.085 3) | ± 0.09 3) | ± 0.10 3) | ± 0.12 3) | ± 0.20 | ± 0.13 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.18 | ± 0.30 | ± 0.20 |
| 1.0 | 1.5 | ± 0.10 4) | ± 0.10 4) | ± 0.10 4) | ± 0.15 4) | ± 0.20 | ± 0.13 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.18 | ± 0.30 | ± 0.20 |
| 1.5 | 2.5 | on request | ± 0.13 5) | ± 0.15 5) | ± 0.16 5) | ± 0.25 | ± 0.18 | ± 0.30 | ± 0.20 | ± 0.35 | ± 0.20 |
| 2.5 | 2.6 | on request | on request | ± 0.16 | ± 0.175 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.18 | ± 0.30 | ± 0.20 | ± 0.35 | ± 0.25 |
| 2.6 | 4.1 | on request | on request | ± 0.16 | ± 0.175 | ± 0.30 | ± 0.20 | ± 0.35 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.40 | ± 0.30 |
| 4.1 | 6.1 | on request | on request | ± 0.16 | ± 0.175 | ± 0.35 | ± 0.25 | ± 0.40 | ± 0.30 | ± 0.45 | ± 0.35 |
1) Other, closer dimensional tolerances are possible under a commercial agreement
2) Including the value t= 0.4
3) Including the value t= 1
4) Including the value t= 1.5
5) Including the value t= 2.5
LENGTH TOLERANCES
| Length tolerances | Closer tolerances are possible under a commercial agreement | Positive tolerance in relation to the nominal length, according to the EN 10140 Standard for the | |
| Nominal length L | Class A | Class B | |
| L ≤ 1000 | + 2 | + 10 | + 6 |
| 1000 < L ≤ 2500 | +0,002L | + 0.01 L | + 6 |
| L > 2500 | +0,002L | + 0.01 L | + 0.003 L |
Sizes in mm.
EDGE CAMBER TOLERANCES
| Nominal width (w) | Closer edge curve tolerances possible under a commercial agreement | Edge curve tolerances according to the EN 10140 Standard | ||
| Maximum deviation 1000 mm | ||||
| Thickness t | Class A (Normal) (maximum deviation) | Class B (FS) (Reduced) (maximum deviation) | ||
| t ≤ 1.20 mm | t > 1.20 mm | |||
| 3 ≤ W < 6 | 2.50 | 4.00 | - | - |
| 6 < W ≤ 10 | 2.00 | 3.00 | - | - |
| 10 < W ≤ 20 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 5.00 | 2.00 |
| 20 < W < 25 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 5.00 | 2.00 |
| 25 ≤ W < 40 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 3.50 | 1.50 |
| 40 ≤ W < 125 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.50 | 1.25 |
| 125 ≤ W ≤ 350 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
| 350 < W < 600 | - | - | 2.00 | 1.00 |
Sizes in mm.
The absolute value of the tolerance can be divided within that range.
RIPPLE - LONGITUDINAL FLATNESS




 The global electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by a number of...
The global electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by a number of...